 Trade Data
Trade Data
 28-06-2024
28-06-2024
Trade data plays a crucial role in understanding global economic trends, evaluating market potential, and making informed business decisions. It encompasses a wide range of information related to the exchange of goods and services between countries. This article will explore the different types of trade data, their significance, and how they can be utilized effectively.

1. Import Data
Import data includes detailed records of goods and services brought into a country from foreign markets. Key components of import data are:
Product Descriptions and HS Codes: Detailed descriptions and Harmonized System (HS) codes, which classify traded products.
Import Quantities and Values: Information on the volume and value of goods imported.
Country of Origin: The country from which the goods are exported.
Importing Companies: Names and details of the companies importing the goods.
Import data helps businesses understand the demand for specific products in a country, identify potential suppliers, and analyze competition.
2. Export Data
Export data provides information about goods and services sent from one country to another. It typically includes:
Product Descriptions and HS Codes: Descriptions and classifications of the exported products.
Export Quantities and Values: Data on the volume and value of goods exported.
Destination Countries: Countries to which the goods are exported.
Exporting Companies: Names and details of the companies exporting the goods.
Export data is essential for businesses looking to expand into new markets, understand market trends, and identify potential buyers.
3. Trade Balance Data
Trade balance data reflects the difference between a country's exports and imports. It can be:
Trade Surplus: When a country exports more than it imports.
Trade Deficit: When a country imports more than it exports.
Trade balance data provides insights into a country’s economic health and its competitiveness in the global market.
4. Bilateral Trade Data
Bilateral trade data details the trade relationships between two countries. It includes information on the goods and services exchanged, their quantities, values, and trade balances. This data is crucial for understanding the dynamics of trade agreements, tariffs, and the impact of trade policies.
5. Multilateral Trade Data
Multilateral trade data involves trade information among multiple countries or regions. It encompasses data on trade blocs, such as the European Union (EU) or the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and international organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO). This data helps businesses understand regional trade dynamics and the effects of multilateral trade agreements.
6. Trade in Services Data
Trade in services data includes information on the exchange of services between countries, such as:
Financial Services: Banking, insurance, and investment services.
Travel and Tourism: Data on expenditures related to travel and tourism.
Telecommunications: Information on cross-border telecommunications services.
Professional Services: Legal, accounting, and consulting services.
This data is increasingly important as the global economy shifts towards more service-oriented activities.
7. Customs Data
Customs data comprises detailed records maintained by customs authorities, including:
Declarations: Information provided by importers and exporters on goods being traded.
Duties and Taxes: Data on tariffs, duties, and taxes levied on goods.
Compliance Information: Records of compliance with trade regulations and standards.
Customs data is vital for ensuring compliance with trade regulations, analyzing trade flows, and monitoring the effectiveness of trade policies.
8. Trade Statistics
Trade statistics aggregate various types of trade data to provide a comprehensive overview of trade activities. They include:
Trade Volumes: Total quantities of goods and services traded.
Trade Values: Total monetary value of goods and services traded.
Trade Indices: Measures of trade performance, such as export and import price indices.
Trade statistics are essential for macroeconomic analysis, policy-making, and business strategy development.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of trade data is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and economists to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies. By leveraging import and export data, trade balance information, bilateral and multilateral trade data, trade in services, customs data, and comprehensive trade statistics, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into global trade dynamics. Utilizing this data effectively can drive business growth, inform policy decisions, and contribute to a deeper understanding of the global economy.
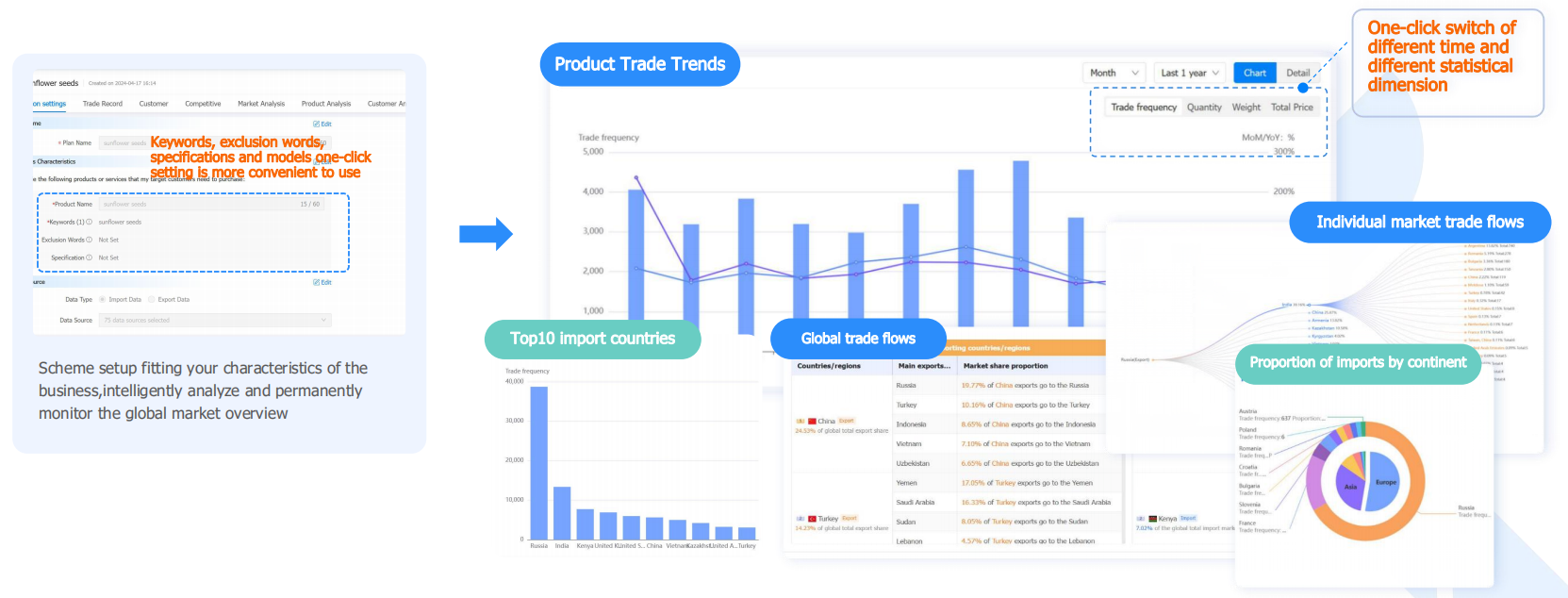
From traditional data retrieval to constructing business scenarios, Tendata T-Insight employs multiple analysts to work for you.
With intelligent market analysis, it assists in saving analysts' time and your money.
Eliminate the need for manual and frequent searches and analyses. With Tendata, you can effortlessly grasp product trade trends, trade flows, top 10 import and export countries with a single click, understand market trends, and identify high-value regions.
Category
Leave Message for Demo Request or Questions


 T-info
T-info T-discovery
T-discovery

 My
Tendata
My
Tendata Market Analysis
Market Analysis Customer
Development
Customer
Development Competitor
Monitoring
Competitor
Monitoring Customer Relationship
Customer Relationship





































































































































