 Market Insights
Market Insights
 07-08-2024
07-08-2024
In today's interconnected world, the role of the global manufacturer has become increasingly vital to the global economy. As companies seek to expand their reach and capitalize on international opportunities, understanding the intricacies of global manufacturing is essential. This article delves into the key aspects of being a global manufacturer, the challenges faced, and the strategies employed to thrive in a dynamic marketplace.

The Scope of Global Manufacturing
Global manufacturing involves the production of goods in multiple countries, leveraging the comparative advantages of different regions. This approach allows companies to optimize costs, access diverse markets, and mitigate risks associated with relying on a single location. For instance, a company might source raw materials from Africa, manufacture components in Asia, and assemble the final product in Europe, all while targeting consumers in North America.
Key Drivers
Cost Efficiency: One of the primary drivers of global manufacturing is cost efficiency. By locating production facilities in countries with lower labor costs, companies can significantly reduce their operational expenses. Additionally, proximity to raw materials and favorable trade agreements can further enhance cost savings.
Market Access: Establishing a presence in various regions allows manufacturers to better serve local markets. This proximity to consumers can lead to faster delivery times, reduced shipping costs, and the ability to tailor products to meet regional preferences and regulations.
Risk Diversification: Relying on a single manufacturing location can be risky due to potential disruptions such as natural disasters, political instability, or supply chain issues. By diversifying production across multiple countries, companies can mitigate these risks and ensure continuity of operations.
Challenges Faced by Global Manufacturers
Complex Supply Chains: Managing a global supply chain is a complex task that requires coordination across different time zones, languages, and cultures. Ensuring the timely delivery of raw materials, components, and finished products can be challenging, especially in the face of unexpected disruptions.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the regulatory landscape in multiple countries can be daunting. Each region has its own set of laws and standards related to labor, environmental impact, and product safety. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal issues and maintain a positive reputation.
Quality Control: Maintaining consistent product quality across different manufacturing sites can be difficult. Variations in local manufacturing practices, equipment, and expertise can impact the final product. Implementing robust quality control measures is essential to ensure uniformity and meet customer expectations.
Strategies for Success
Investing in Technology: Embracing advanced technologies such as automation, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) can streamline manufacturing processes and enhance efficiency. These technologies enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making.
Building Strong Partnerships: Collaborating with local partners, suppliers, and governments can provide valuable insights and resources. Strong relationships can facilitate smoother operations, better compliance with local regulations, and improved access to regional markets.
Sustainability Initiatives: Adopting sustainable practices is becoming increasingly important for global manufacturers. Reducing carbon footprints, minimizing waste, and sourcing eco-friendly materials not only benefit the environment but also enhance brand reputation and meet the growing demand for green products.
Agile Supply Chains: Developing an agile and responsive supply chain can help manufacturers quickly adapt to changes in demand, geopolitical events, and other disruptions. Flexibility in sourcing, production, and distribution is key to maintaining resilience in a volatile global market.
Conclusion
The global manufacturer plays a pivotal role in the modern economy, driving innovation, economic growth, and consumer access to diverse products. While the path to success is fraught with challenges, strategic investments in technology, partnerships, sustainability, and supply chain agility can empower manufacturers to navigate the complexities of the global marketplace. By leveraging these strategies, global manufacturers can continue to thrive and contribute to a more interconnected and prosperous world.
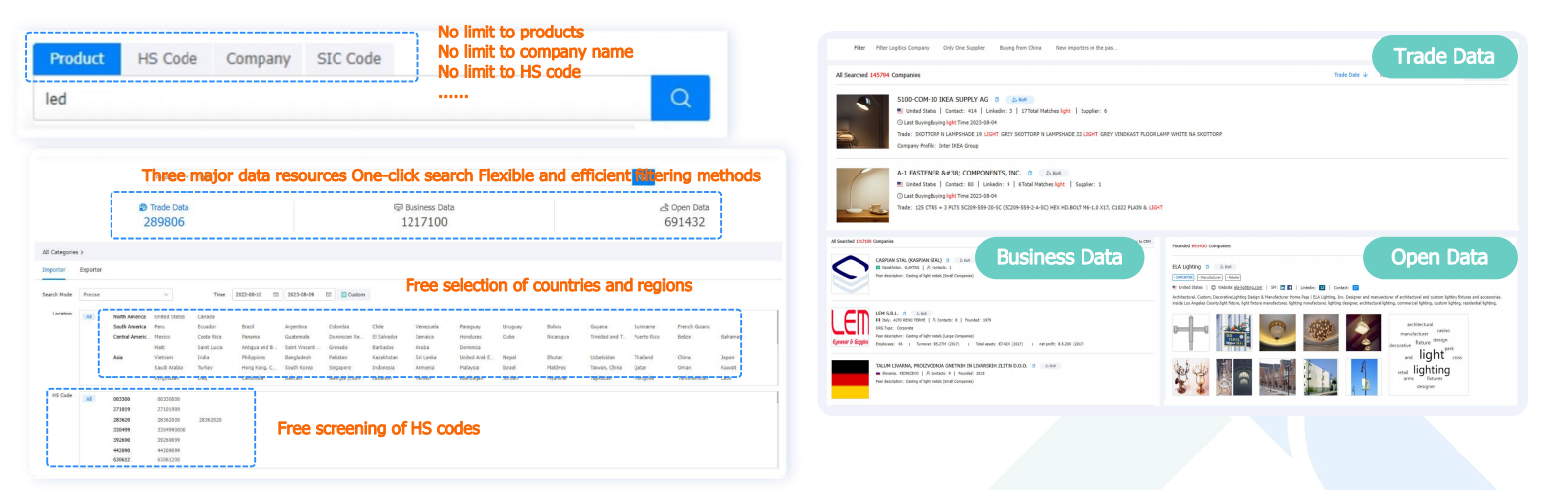
Capture Global Customers with One Click and Precisely Target Potential Business Opportunities
Tendata T-Discovery leverages robust data resources as its foundation, seamlessly integrating trade data, business data, and internet data. Breaking through data barriers, it offers pragmatic and convenient solutions, enabling direct access to target customer groups through authentic trade transaction data. This facilitates comprehensive understanding of both existing and potential buyers in the target market, swiftly identifying suitable customer groups for development.
Three robust data resources, one-click connectivity, multiple filtering methods, and flexible, efficient visual presentation of results make T-Discovery stand out prominently.
1. Trade Data: Conduct market research, predict product trends, develop and maintain customer relationships, monitor industry trends, and set pricing strategies.
2. Business Data: Access enterprise details, operational status, shareholder information, business reputation, financial status, and contact details.
3. Internet Data: Explore global enterprise products, pinpoint company information accurately, access a wide array of contact information (key personnel and positions, phone numbers, official websites, emails, addresses, etc.), and link to major social media platforms (LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, etc.).
Category
Leave Message for Demo Request or Questions


 T-info
T-info T-discovery
T-discovery

 My
Tendata
My
Tendata Market Analysis
Market Analysis Customer
Development
Customer
Development Competitor
Monitoring
Competitor
Monitoring Customer Relationship
Customer Relationship




































































































































