 Market Insights
Market Insights
 21-06-2024
21-06-2024
Foreign trade, also known as international trade, involves the exchange of goods, services, and capital between countries. It is a complex system that facilitates the flow of products and services across borders, enabling nations to specialize in the production of goods where they have a competitive advantage. Here's a detailed look at how foreign trade works:

1. Concept of Comparative Advantage
Foreign trade is primarily driven by the concept of comparative advantage. This economic theory suggests that countries should produce and export goods and services they can produce more efficiently (at a lower opportunity cost) and import goods that other countries produce more efficiently. This specialization increases global production efficiency and benefits all trading partners.
2. Key Players in Foreign Trade
Exporters: Individuals or companies that sell goods and services to foreign markets.
Importers: Individuals or companies that purchase goods and services from foreign markets.
Governments: They regulate trade through policies, tariffs, and trade agreements to protect national interests and promote economic growth.
Trade Organizations: Entities like the World Trade Organization (WTO) facilitate and regulate international trade agreements and disputes.
3. Trade Agreements and Policies
Countries often enter into trade agreements to promote trade by reducing barriers like tariffs, quotas, and import restrictions. Key types of trade agreements include:
Bilateral Agreements: Between two countries.
Multilateral Agreements: Involving multiple countries (e.g., North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), now replaced by the USMCA).
Regional Trade Agreements: Among countries in a specific region (e.g., European Union (EU), ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA)).
4. Trade Processes
The process of foreign trade involves several steps:
Market Research and Planning:
Identify Demand: Businesses conduct research to identify demand for their products in foreign markets.
Regulations: Understanding the regulations, standards, and certifications required for export/import.
Finding Trade Partners:
Networking: Use trade fairs, business associations, and online platforms to find potential buyers/sellers.
Due Diligence: Assess the credibility and reliability of trade partners.
Negotiation and Contracts:
Terms of Trade: Agree on the terms, including price, quantity, delivery, and payment methods.
Contracts: Draft legally binding contracts to ensure all parties adhere to the agreed terms.
Logistics and Shipping:
Transport: Arrange transportation of goods via sea, air, rail, or road.
Documentation: Prepare necessary documents such as commercial invoices, packing lists, bills of lading, and certificates of origin.
Customs Clearance:
Export Customs: Goods are cleared by customs authorities in the exporting country.
Import Customs: Goods are inspected and cleared by customs in the importing country. Duties and taxes may be applicable.
Payment:
Methods: Common payment methods include letters of credit (LC), advance payment, and open accounts.
Currency Exchange: Managing currency exchange risks through forward contracts or other financial instruments.
Delivery and Distribution:
Warehousing: Goods may be stored in warehouses before final delivery.
Distribution: Goods are distributed to the final consumers through various channels.
5. Challenges in Foreign Trade
Cultural Differences: Understanding and adapting to cultural differences in business practices.
Economic Fluctuations: Dealing with currency exchange rate volatility and economic instability.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex international laws and regulations.
Logistics Issues: Managing transportation, warehousing, and delivery logistics efficiently.
Foreign trade is a vital component of the global economy, enabling countries to access goods and services not available domestically, achieve economic growth, and foster international relations. By understanding the principles, processes, and challenges involved, businesses and governments can effectively engage in and benefit from international trade.
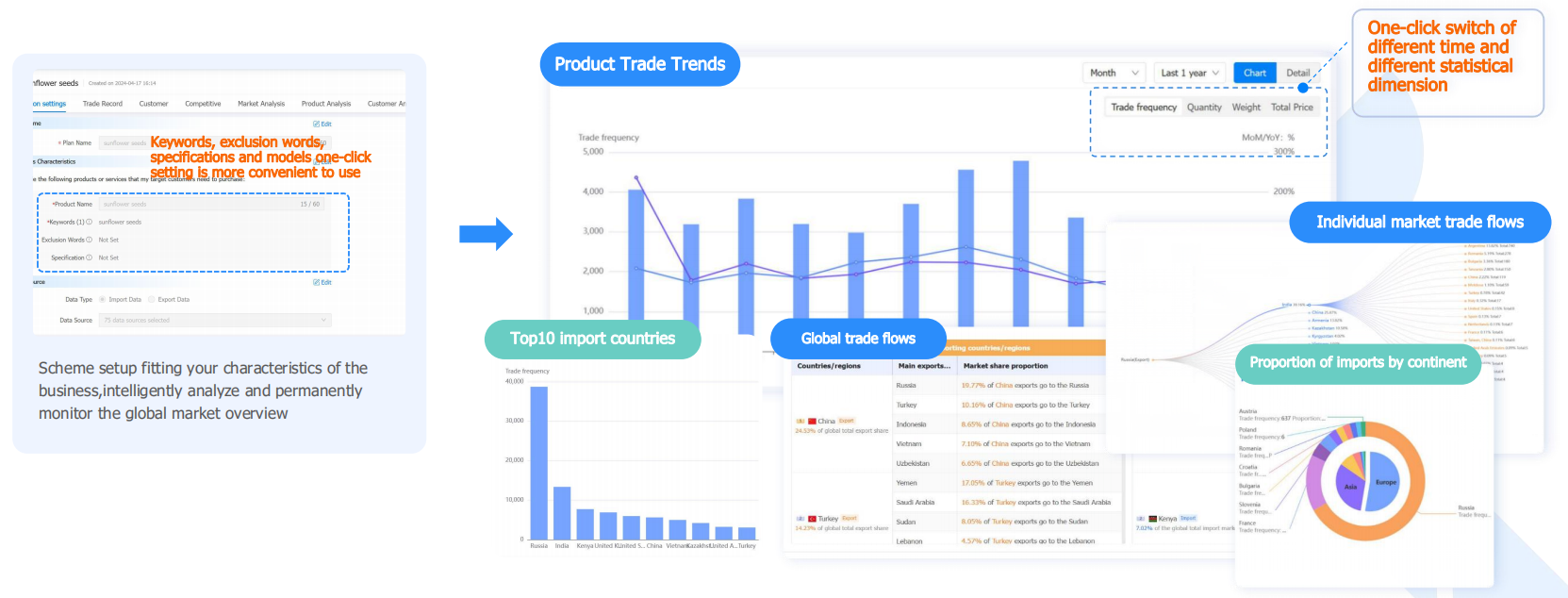
From traditional data retrieval to constructing business scenarios, Tendata T-Insight employs multiple analysts to work for you.
With intelligent market analysis, it assists in saving analysts' time and your money.
Eliminate the need for manual and frequent searches and analyses. With Tendata, you can effortlessly grasp product trade trends, trade flows, top 10 import and export countries with a single click, understand market trends, and identify high-value regions.
Category
Leave Message for Demo Request or Questions


 T-info
T-info T-discovery
T-discovery

 My
Tendata
My
Tendata Market Analysis
Market Analysis Customer
Development
Customer
Development Competitor
Monitoring
Competitor
Monitoring Customer Relationship
Customer Relationship





































































































































