 Import News
Import News
 26-11-2024
26-11-2024
In 2023, South Africa's imports data paints a compelling picture of the nation’s evolving trade dynamics and economic landscape. As a cornerstone of the African economy, South Africa's import activities play a pivotal role in shaping various industries, supporting local manufacturing, and meeting consumer demands. The analysis of South African imports data reveals key trends, strategic shifts in trade partnerships, and implications for businesses operating in this complex market.

Understanding South Africa's Imports Data
The total volume of South Africa's imports in 2023 illustrates resilience and adaptability, even amid global economic uncertainties. Comprehensive data indicates that the nation's imports remain dominated by several critical categories, including raw materials, machinery, and finished goods.
Machinery and Equipment: This category continues to be a significant contributor to South Africa's imports data, reflecting the country's ongoing investments in infrastructure and industrial development.
Electrical Machinery: As technology advances, the demand for electrical machinery surges. This trend is prominent in South African imports data, showcasing the nation's push toward modernization.
Mineral Products: Leveraging its rich resource base, South Africa imports various mineral products to complement local industries, particularly when domestic supply falls short.
Chemical Products: Essential for sectors like manufacturing and pharmaceuticals, chemical products remain a significant part of South Africa's imports data, highlighting the interconnectedness of global supply chains.
>>Click for South Africa's Import Data<<
Top South African Imports in 2023:
· HS Code 2710 (14.1%, $15.1 billion): Petroleum oils and oils from bituminous minerals, not crude; preparations n.e.c. containing by weight 70% or more of petroleum oils or oils from bituminous minerals; these being the basic constituents of the preparations; waste oils
· HS Code 2709 (4.48%, $4.8 billion): Petroleum oils and oils obtained from bituminous minerals, crude
· HS Code 8703 (3.83%, $4.1 billion): Motor cars and other motor vehicles principally designed for the transport of persons (other than those of heading 87.02), including station wagons and racing cars
· HS Code 8517 (2.92%, $3.13 billion): Electrical apparatus for line telephony or line telegraphy, including line telephone sets with cordless handsets and telecommunication apparatus for carrier-current line systems or for digital line systems; videophones
· HS Code 8507 (1.86%, $1.99 billion): Electric accumulators, including separators therefor, whether or not rectangular (including square)
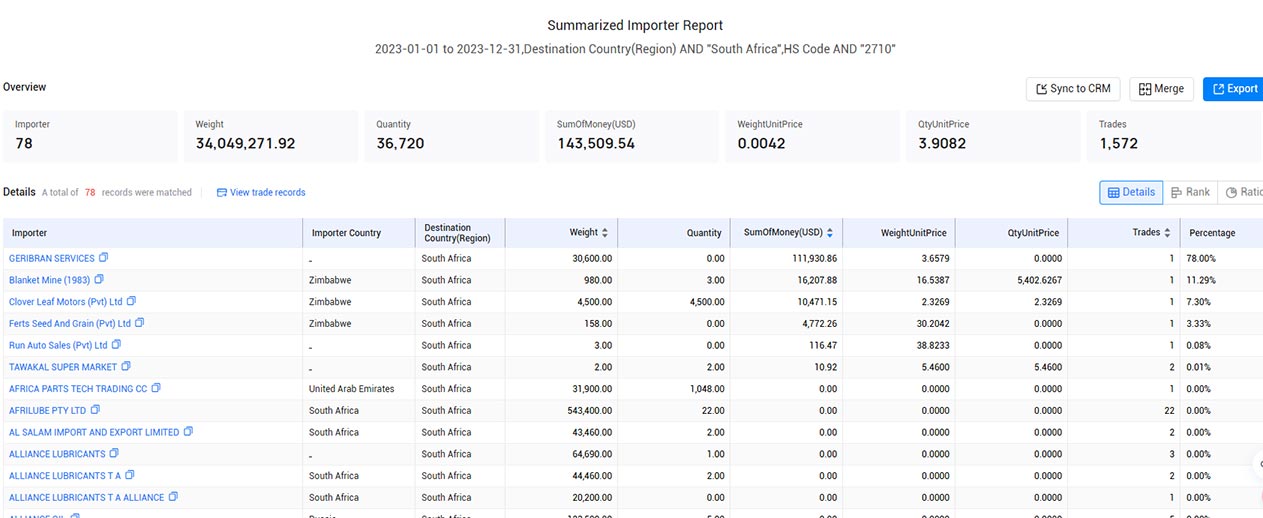
· HS Code 8471 (1.82% ($1.95 billion): Automatic data processing machines and units thereof; magnetic or optical readers, machines for transcribing data onto data media in coded form and machines for processing such data, not elsewhere specified or included
· HS Code 8708 (1.72%, $1.84 billion): Parts and accessories of the motor vehicles of headings 87.01 to 87.05
· HS Code 4907 (1.67%, $1.79 billion): Unused postage, revenue or similar stamps of current or new issue in the country in which they have, or will have, a recognised face value; stamp-impressed paper; banknotes; cheque forms; stock, share or bond certificates and similar documents of title.
· HS Code 3004 (1.6%, $1.71 billion): Medicaments (excluding goods of heading 30.02, 30.05 or 30.06) consisting of mixed or unmixed products for therapeutic or prophylactic uses, put up in measured doses (including those in the form of transdermal administration systems) or in forms or packings for retail sale.
>>Click Here for South Africa's Import Data<<
Key Trends Influencing South African Imports Data
Evolving Trade Relationships: In 2023, South Africa has been actively diversifying its trading partners. Notable increases in imports from countries in Asia, particularly China and India, reflect a shift in the global supply chain dynamics and a reduction in reliance on traditional markets.
Global Supply Chain Disruptions: The effects of the pandemic and geopolitical tensions are still influencing South Africa's imports data. Businesses are adapting their sourcing strategies to mitigate risks associated with supply chain uncertainties, prompting a reevaluation of import practices.
Technological Advancements: The rapid digitization of the economy has led to an increase in imports related to technology. South African imports data shows a rising demand for digital goods and tech services, reflecting a broader transformation in the nation's business landscape.
Why Utilize Tendata?
In-depth Import Analytics: Tendata provides extensive access to South African imports data, allowing businesses to analyze trends and identify opportunities.
Real-time Access: With real-time data, companies can swiftly adapt to changing market dynamics, ensuring they make informed decisions on sourcing and logistics.
User-friendly Interface: Tendata offers an intuitive design, making it accessible even for non-technical users who seek to leverage the wealth of data.
Customizable Dashboards: Users can create tailored dashboards to visualize pertinent trends in South African imports data, allowing them to focus on metrics that are critical to their operations.
Expert Insights: Beyond raw data, Tendata offers expert analysis, equipping businesses with a deeper understanding of the implications associated with South African imports data, facilitating smarter strategic planning.
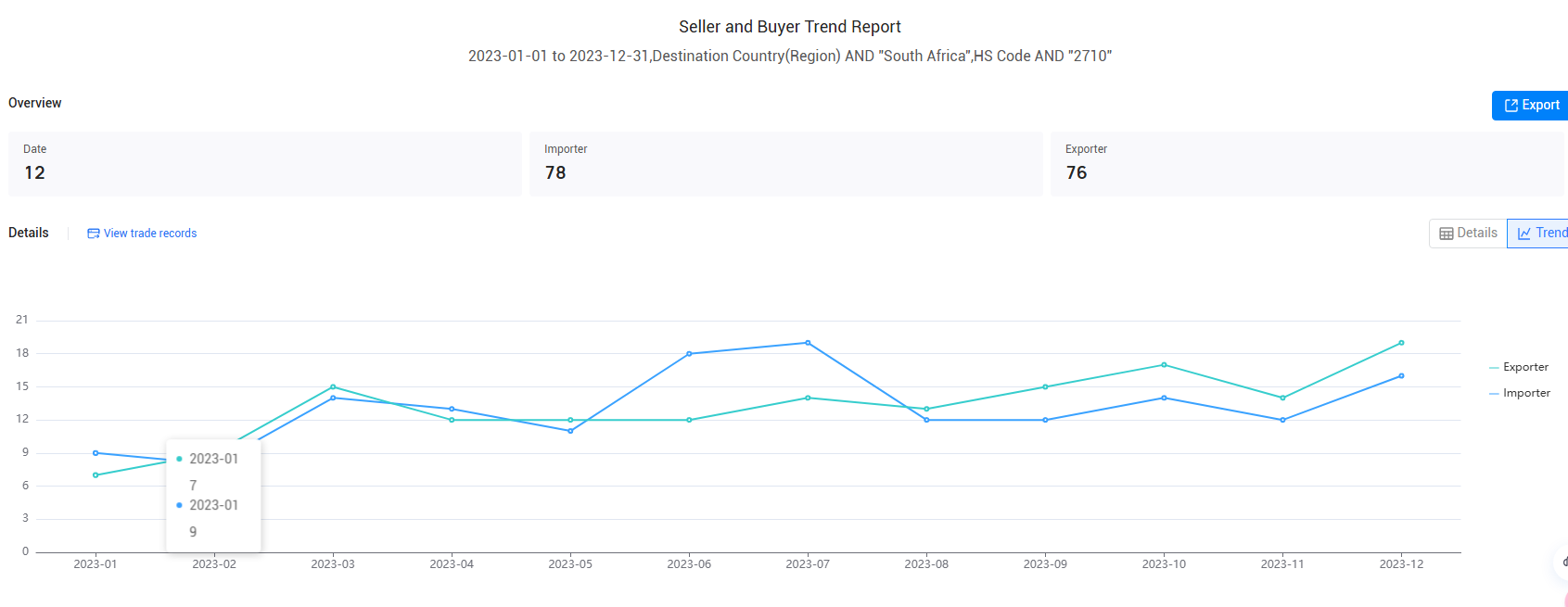
Conclusion
As South Africa continues to navigate its way through 2023, its imports data illustrates a landscape filled with both challenges and opportunities. The strategic use of accurate data is essential for businesses looking to thrive in an increasingly competitive global market. By leveraging Tendata, companies can gain invaluable insights into South Africa's imports data, guiding them in decision-making processes and enhancing their competitive edge. >>Contact Tendata for online demo<<

Category
Leave Message for Demo Request or Questions


 T-info
T-info T-discovery
T-discovery

 My
Tendata
My
Tendata Market Analysis
Market Analysis Customer
Development
Customer
Development Competitor
Monitoring
Competitor
Monitoring Customer Relationship
Customer Relationship






































































































































